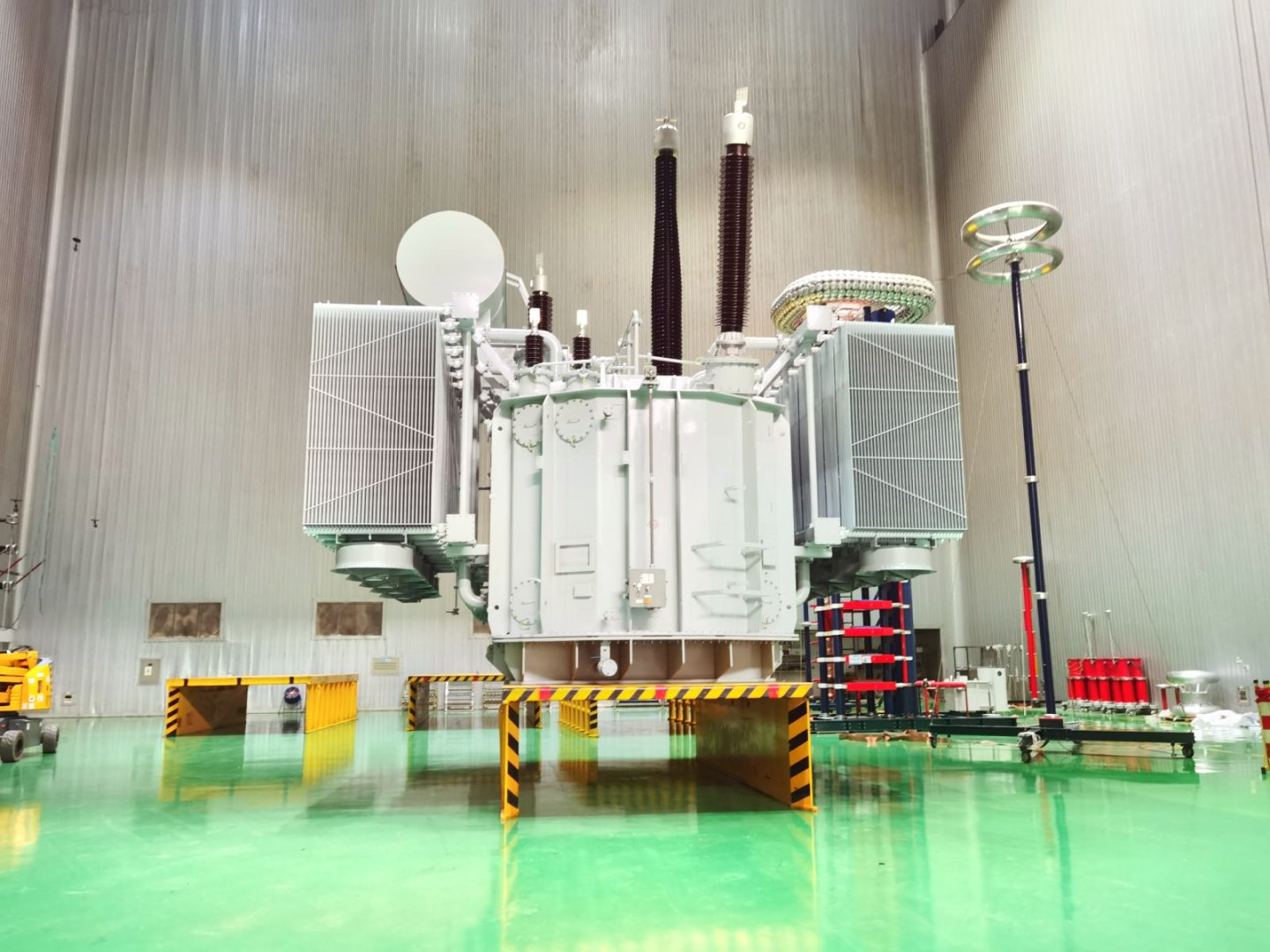
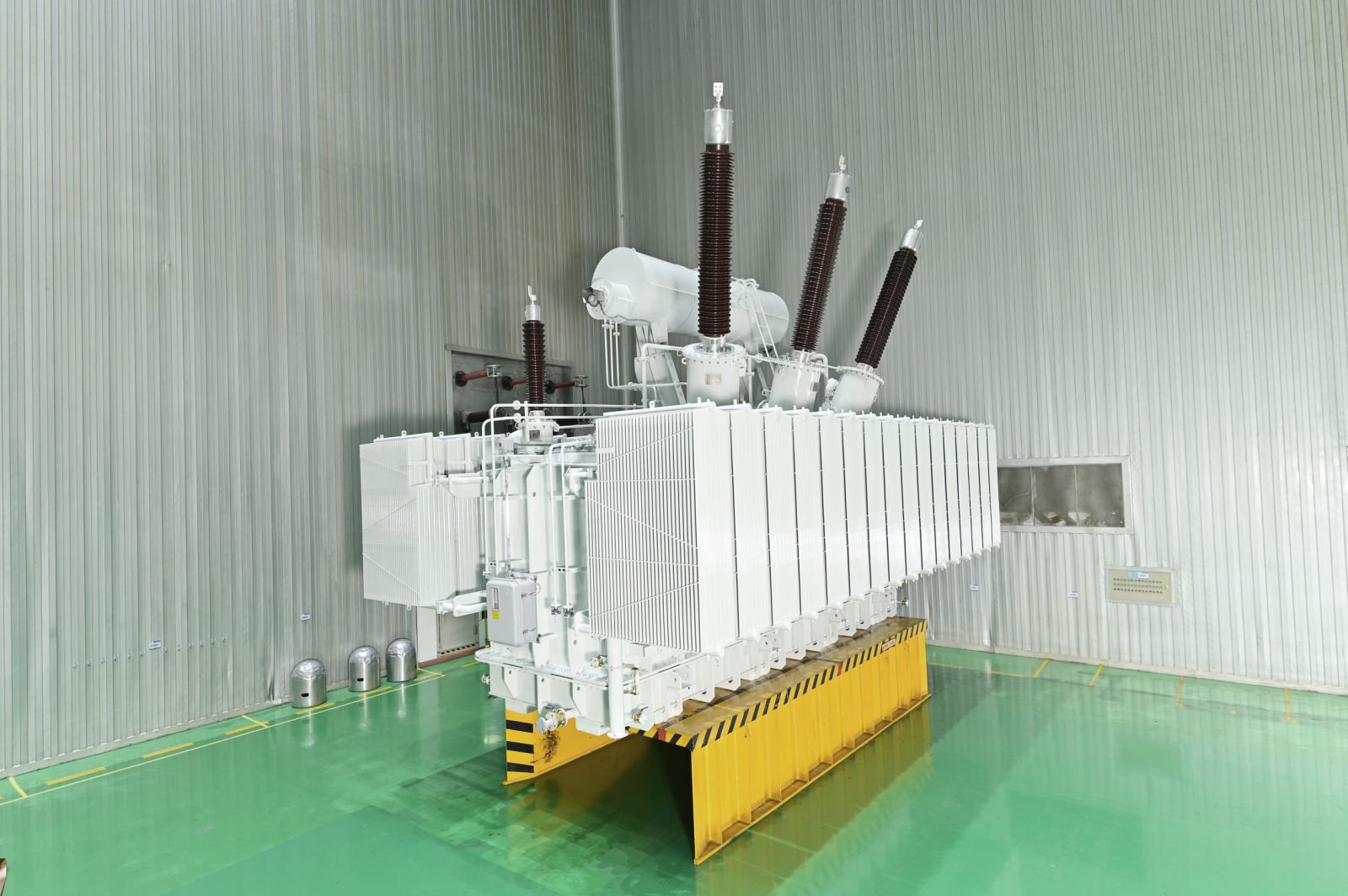
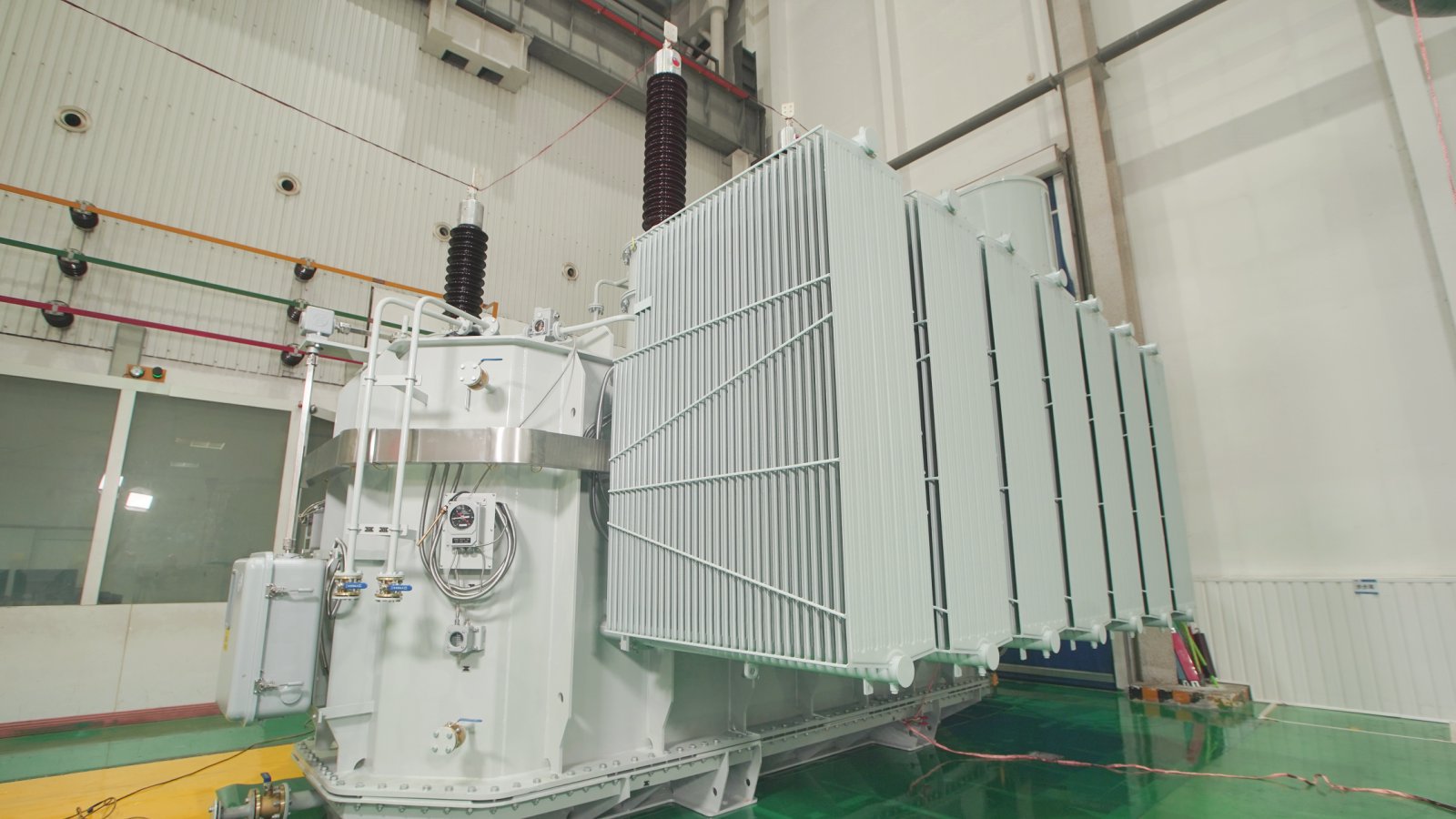
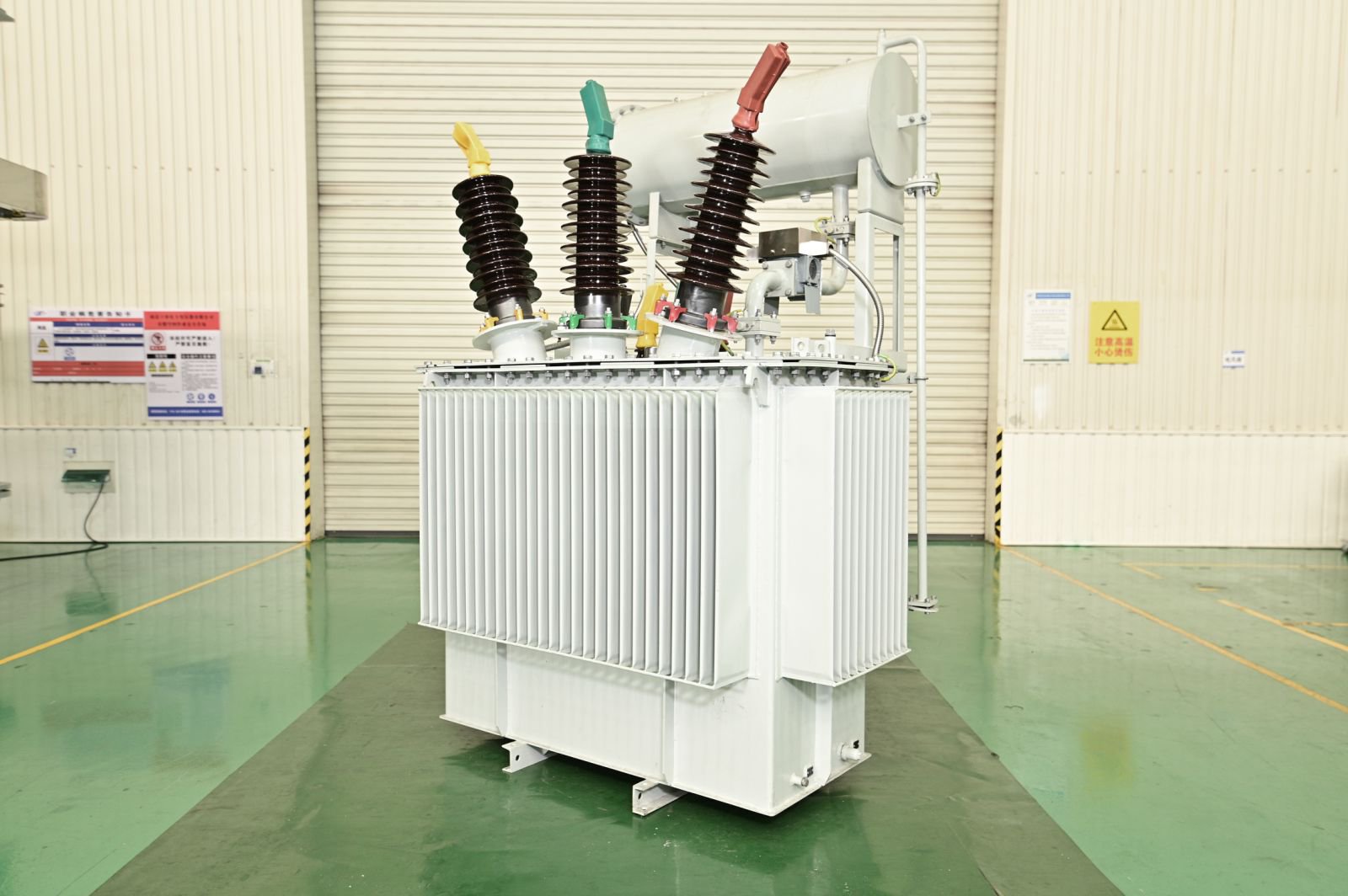
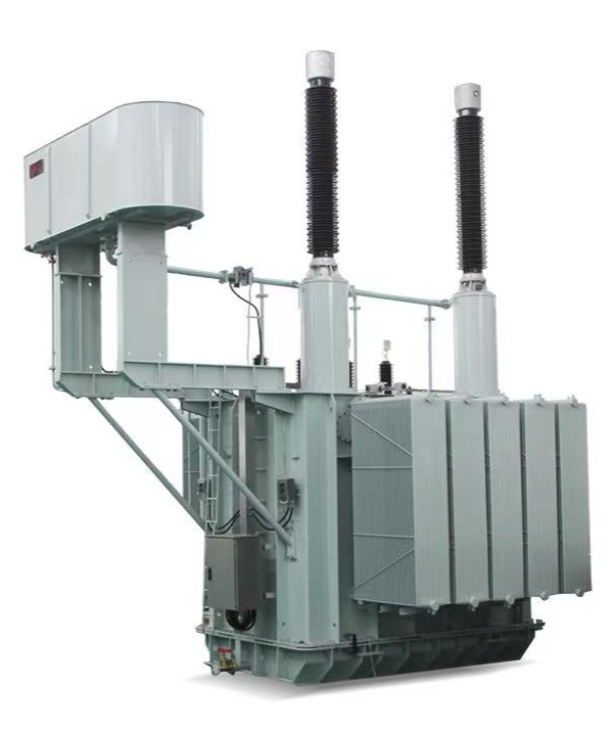
The secondary winding of a split transformer comprises multiple independent branches, each separated by high impedance. This design enables each branch to supply power independently, thereby reducing mutual interference and enhancing system reliability and flexibility. It is commonly employed in power stations, large industrial equipment, and other applications requiring multiple independent power sources.